15 Paired t-test and Wilcoxon Signed Ranks
Paired t-test
The paired t-test is used for analyses with a continuous dependent variable and a categorical independent variable but only when a within-participants (repeated measures) design is used.
Note: The paired t-test can only be used to compare the differences in the means of two variables for the same group of participants. More advanced tests are needed for designs with more than one group and/or more than 3 variables.
How do I do that?
1. In the ‘T-Test’ menu select Paired Samples T-Test from the ‘Classical’ list.
2. A new window will open, like so:
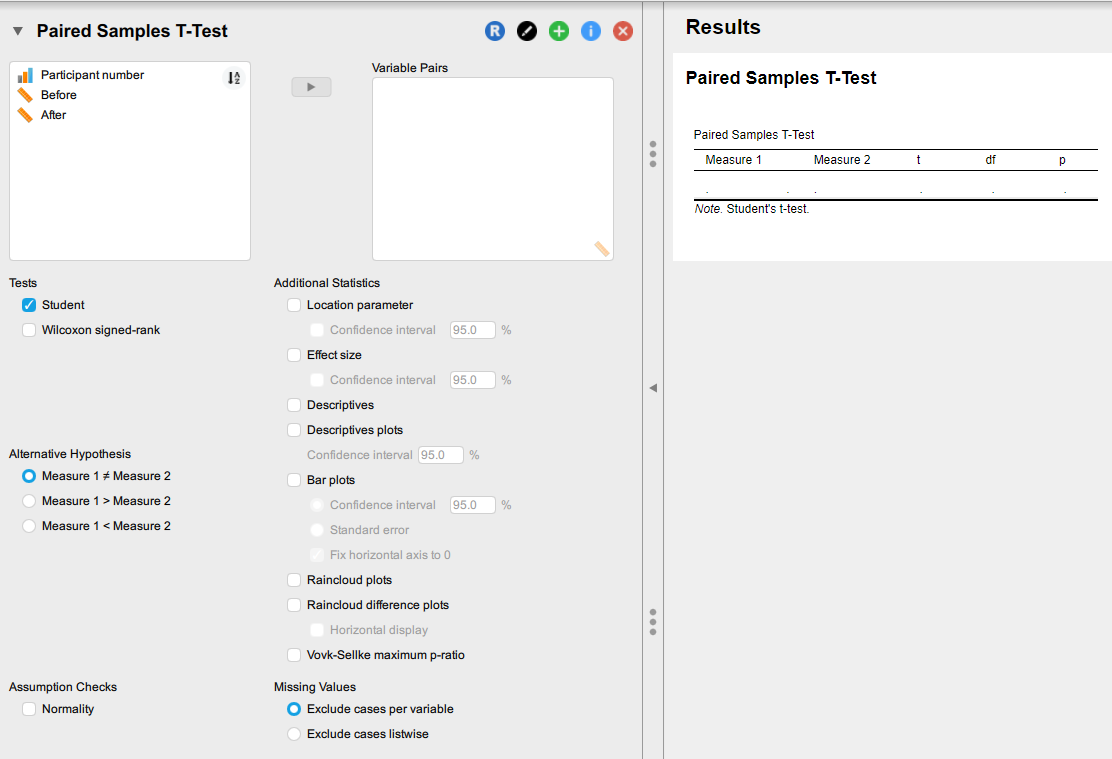
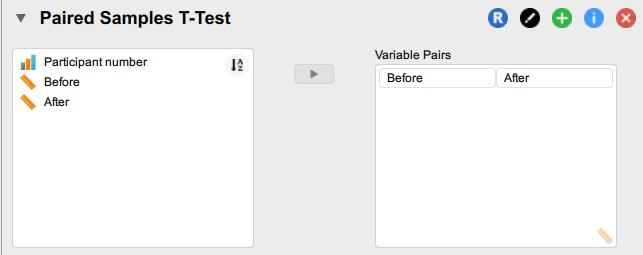
3. Move the two variables you wish to compare over to the Variable Pairs box.
4. There are many options in the expandable menus for this type of analysis which can initially be overwhelming. However, it is unlikely that you will need all of them. Here are some of the t-test options which you are likely to use:
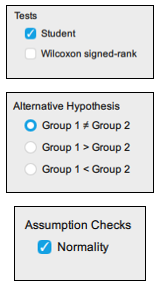
Tests. The ‘Student’ test is the default but if you have non-parametric data, you need to select the ‘Wilcoxon Signed Ranks’ test.
Alternative Hypothesis. The default is the hypothesis that Group 1 ≠ Group 2. This is the non-directional hypothesis and for most cases, you will not change this. You can see that there are two options for the directional hypotheses.
Assumption Checks. These help you decide whether any of the assumptions for conducting a paired t-test have been violated. As this is a paired t-test which looks at the difference between the same group of people, the test for equality of variances is not needed so you only need to check ‘Normality’. The Test of Normality statistic is Shapiro Wilk (W). A significant Shapiro Wilk tells you that the distribution significantly differs from normal and that the assumption of normality has likely been violated. You will then need to conduct a Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test (covered in the next section).
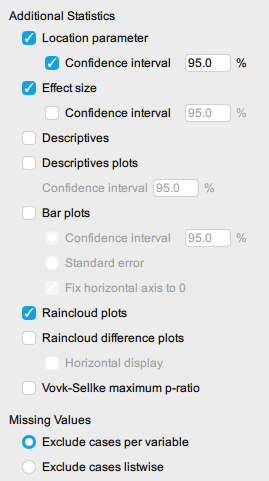 Additional Statistics. These provide you with additional information about your results. Unless instructed otherwise, it is usually a good idea to generate the following additional statistics:
Additional Statistics. These provide you with additional information about your results. Unless instructed otherwise, it is usually a good idea to generate the following additional statistics:
-
-
-
- Select Location parameter and Confidence Interval.
- Selecting Effect Size will select Cohen’s d (although this is not stated).
- Selecting Descriptives and Descriptive plots will give you some basic descriptives and an error bar plot to help visualise the data.
- Selecting Raincloud plots will give you a rather fantastic set of plots that allows you to visualise the data in a scatterplots, boxplots, and overlayed histograms.
-
-
Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test
If you find that your data is not normally distributed (e.g., you have a significant Shapiro-Wilk test result), you need to conduct the equivalent non-parametric paired t-test called Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test.
How do I do that?
1. Follow Steps 1-3 from the paired t-test and select the Wilcoxon Signed Rank option in the ‘Tests’ menu.
2. As with the paired t-test, the default for Alternative Hypotheses is Group 1 ≠ Group 2. This is the non-directional hypothesis and for most cases, you will not need to change this.
3. In the Analysis options, you will only need to select Effect Size and leave the default as Cohen’s d. In the output table the effect size will be given by the Rank-Biserial Correlation. This can be interpreted in the same way as Pearson’s r
4. You may also want to select ‘Raincloud plots’ as this helps to visualise the data.

